The relationship between temperature and liver health has increasingly become a subject of scientific interest. Celsius, as a unit of temperature measurement, plays a critical role in understanding how heat or cold exposure can affect the liver's functionality. This article aims to provide an in-depth look into how extreme temperatures, measured in Celsius, can lead to liver damage and what steps individuals can take to protect their liver health.
Liver damage caused by temperature extremes is not as widely discussed as other forms of liver injury, such as alcohol abuse or viral hepatitis. However, it is a growing concern, especially as global climate changes expose more people to extreme weather conditions. Understanding how these temperatures affect the liver is vital for safeguarding one of the body's most essential organs.
As we delve deeper into this topic, you'll learn about the mechanisms behind liver damage due to temperature variations, preventive measures, and the importance of maintaining optimal liver health. Whether you're a healthcare professional, a fitness enthusiast, or simply someone interested in health, this article will provide valuable insights into the connection between Celsius and liver damage.
Read also:Comprehensive Guide To Calcasieu Correctional Jail Roster
Table of Contents
- Biological Mechanism of Liver Damage
- Effects of Cold Temperatures on the Liver
- Effects of Heat Temperatures on the Liver
- Temperature Regulation and Liver Function
- Symptoms of Liver Damage Due to Temperature Extremes
- Preventive Measures Against Liver Damage
- Dietary Advice for Liver Health
- Scientific Studies on Temperature and Liver Health
- Risk Groups for Temperature-Induced Liver Damage
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Biological Mechanism of Liver Damage
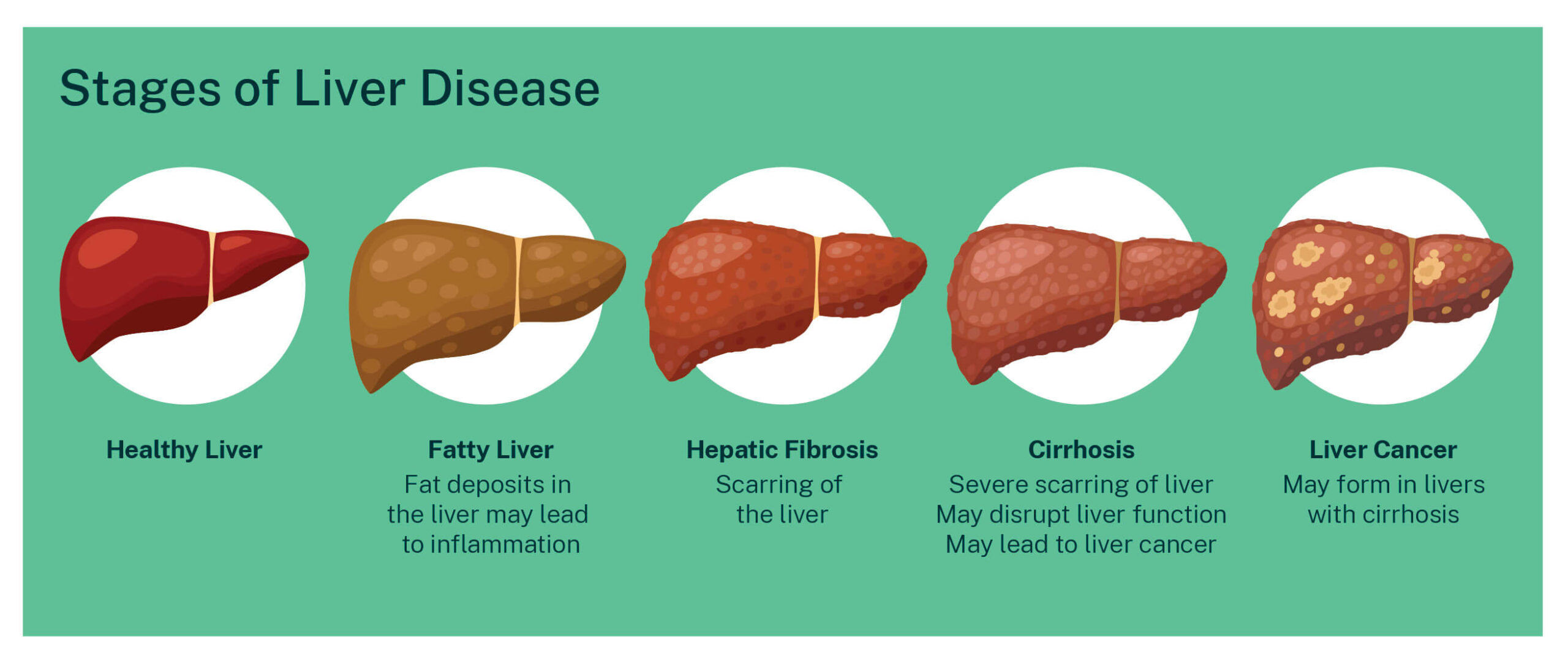
The liver is one of the most critical organs in the human body, responsible for detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion. When exposed to extreme temperatures measured in Celsius, the liver's biological mechanisms can be disrupted, leading to damage. This section explores how temperature extremes affect cellular processes within the liver.
Heat Shock Proteins and Liver Cells
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) play a crucial role in protecting liver cells from thermal stress. When the body is exposed to high temperatures, these proteins are produced to stabilize cellular structures and prevent protein denaturation. However, prolonged exposure to extreme heat can overwhelm the liver's capacity to produce HSPs, resulting in cell damage.
Cold Stress and Liver Metabolism
In contrast, cold temperatures can slow down metabolic processes in the liver. This reduction in metabolism can lead to the accumulation of toxins and waste products, which the liver may struggle to process efficiently. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for developing strategies to mitigate liver damage caused by temperature extremes.
Effects of Cold Temperatures on the Liver
Cold temperatures, particularly those below 10 degrees Celsius, can significantly impact liver function. This section examines the specific effects of cold exposure on the liver and the potential long-term consequences.
- Reduced blood flow to the liver due to vasoconstriction
- Slowed enzymatic activity, affecting digestion and detoxification
- Increased risk of fatty liver disease due to impaired lipid metabolism
Effects of Heat Temperatures on the Liver
Heat exposure, especially temperatures above 40 degrees Celsius, poses a different set of challenges for liver health. This section explores the impact of heat on liver function and the mechanisms behind heat-induced liver damage.
Dehydration and Liver Function
One of the primary effects of heat exposure is dehydration, which can lead to reduced blood volume and increased liver workload. The liver must work harder to filter toxins from the bloodstream, potentially leading to damage over time.
Read also:Peoria Journal Star Pending Obituaries A Comprehensive Guide
Heat Stroke and Liver Injury
Heat stroke, a severe condition caused by prolonged exposure to high temperatures, can cause direct liver injury. This injury is often a result of oxidative stress and inflammation, which can overwhelm the liver's natural defense mechanisms.
Temperature Regulation and Liver Function
The human body has sophisticated mechanisms for regulating temperature, and the liver plays a key role in this process. This section discusses how temperature regulation affects liver function and the importance of maintaining a stable internal environment.
Hypothermia and Hyperthermia
Both hypothermia (low body temperature) and hyperthermia (high body temperature) can disrupt liver function. Understanding these conditions and their effects on the liver is crucial for preventing temperature-induced damage.
Symptoms of Liver Damage Due to Temperature Extremes
Recognizing the symptoms of liver damage caused by temperature extremes is essential for early intervention. This section outlines the common signs and symptoms associated with temperature-related liver injury.
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Fatigue and weakness
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Loss of appetite
Preventive Measures Against Liver Damage
Preventing liver damage caused by temperature extremes involves a combination of lifestyle changes and protective measures. This section provides practical advice for safeguarding liver health in varying temperature conditions.
Staying Hydrated
Hydration is crucial for maintaining liver function, especially in hot weather. Drinking plenty of water helps the liver filter toxins more efficiently and prevents dehydration-related stress.
Dressing Appropriately
Wearing appropriate clothing for the weather can help regulate body temperature and protect the liver from extreme conditions. Layering clothing in cold weather and wearing breathable fabrics in hot weather are simple yet effective strategies.
Dietary Advice for Liver Health
A balanced diet is essential for maintaining liver health, particularly when exposed to temperature extremes. This section offers dietary recommendations to support liver function and protect against damage.
- Consume foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption
- Incorporate omega-3 fatty acids into your diet
Scientific Studies on Temperature and Liver Health
Several scientific studies have investigated the relationship between temperature and liver health. This section highlights key findings from these studies and their implications for public health.
A study published in the Journal of Hepatology found that prolonged exposure to high temperatures can increase the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Another study in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology demonstrated the protective effects of heat shock proteins in mitigating liver damage during heat stress.
Risk Groups for Temperature-Induced Liver Damage
Certain populations are more vulnerable to temperature-induced liver damage. This section identifies these risk groups and discusses why they are more susceptible to liver injury.
- Elderly individuals with reduced thermoregulatory capacity
- People with pre-existing liver conditions, such as cirrhosis
- Outdoor workers exposed to extreme temperatures
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, the relationship between Celsius and liver damage is complex but crucial for understanding how temperature extremes can affect liver health. By recognizing the biological mechanisms behind liver injury, identifying risk groups, and implementing preventive measures, individuals can protect their liver from temperature-induced damage.
We encourage readers to take action by staying informed about temperature-related health risks, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and consulting healthcare professionals for personalized advice. Share this article with others to raise awareness about the importance of liver health and temperature regulation.
For further reading, explore our other articles on health and wellness topics. Together, we can promote a healthier, more informed community.